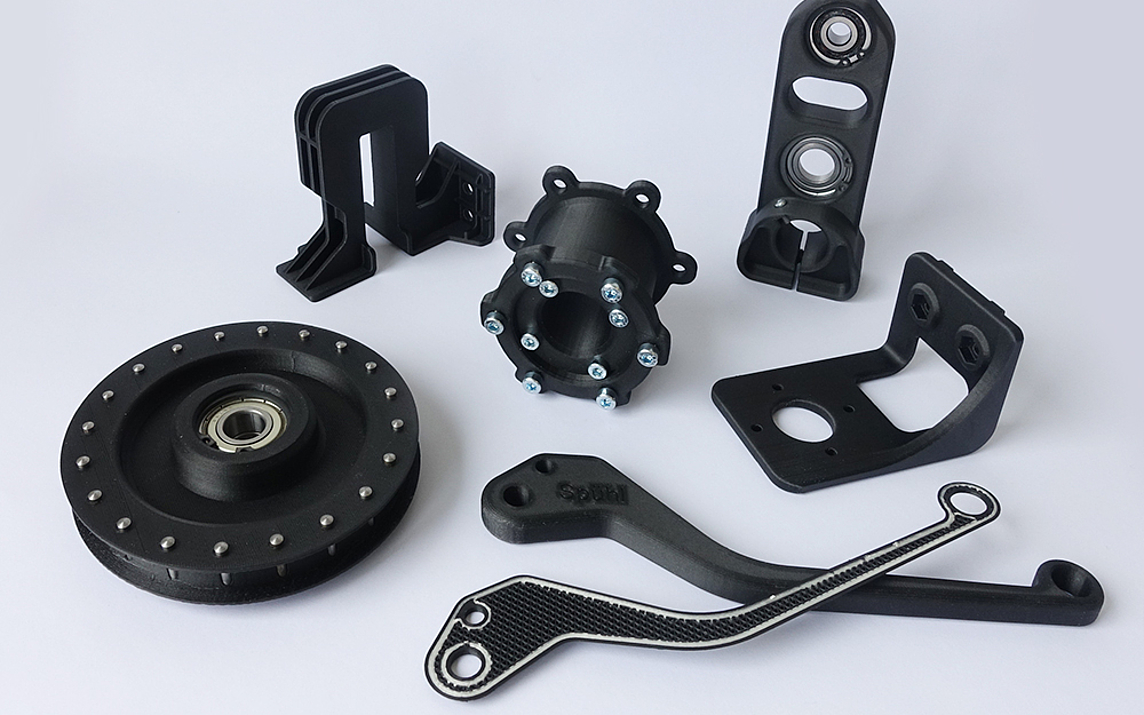
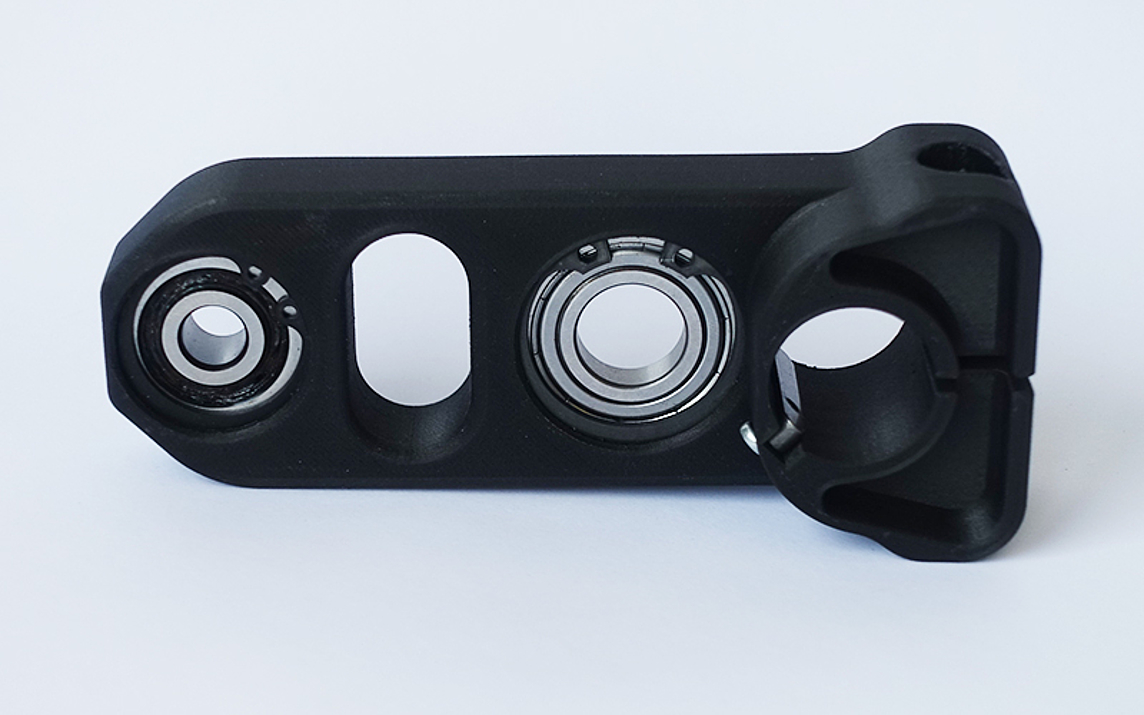
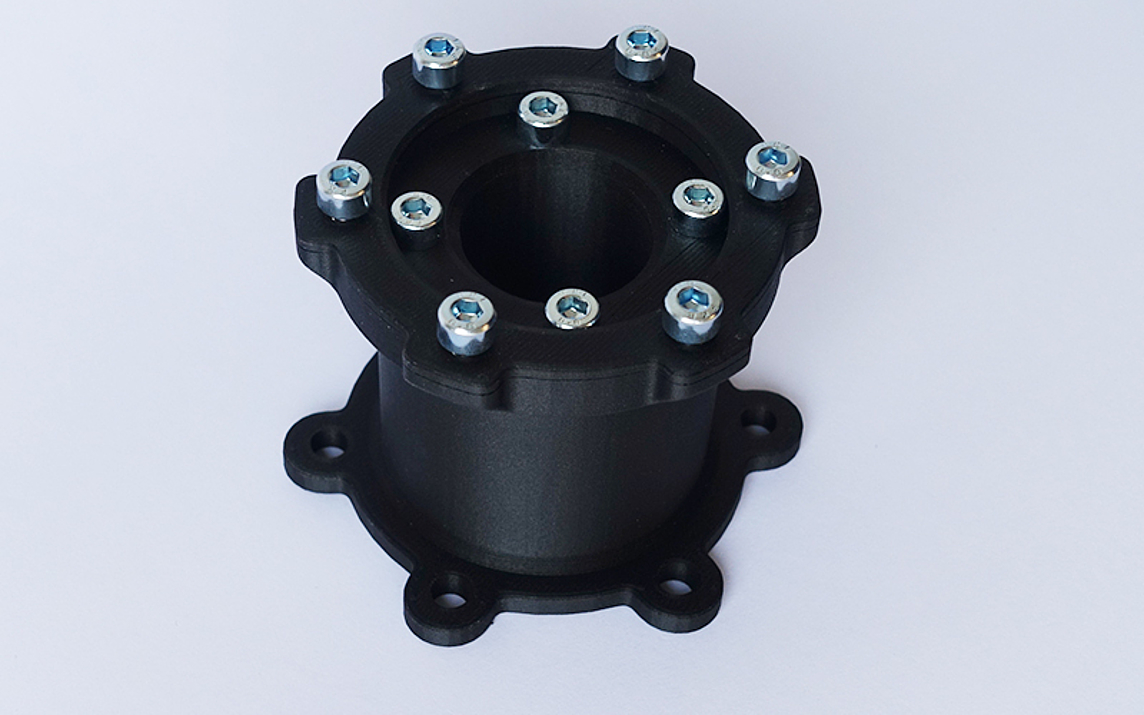
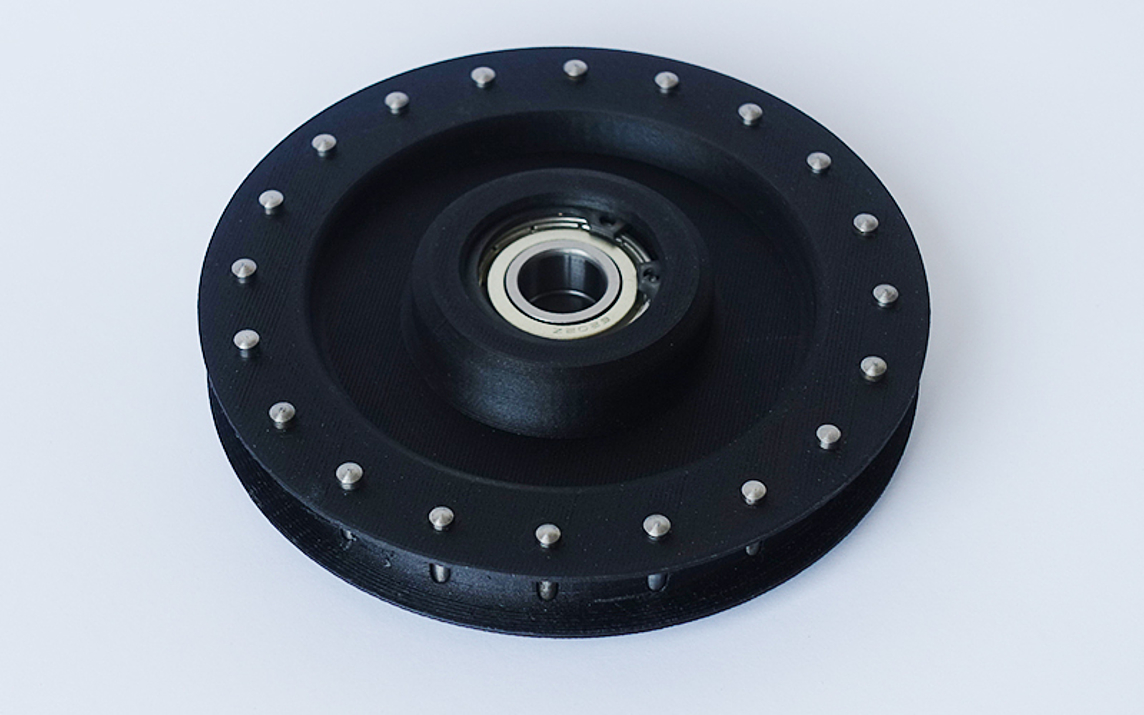
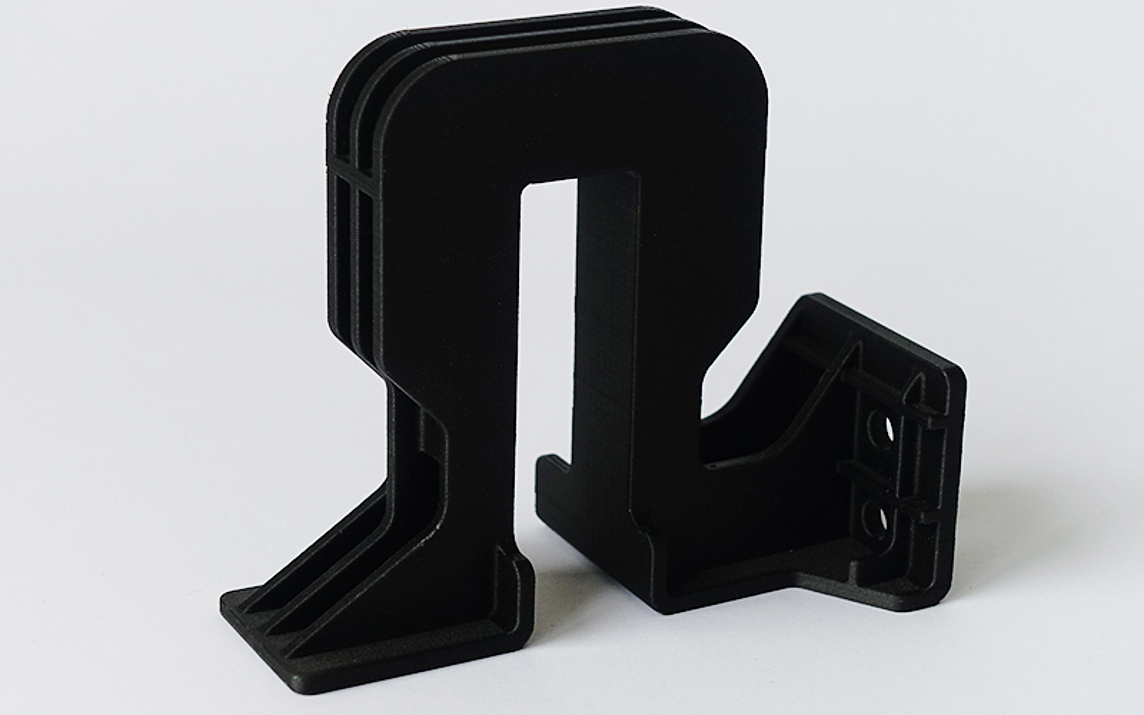
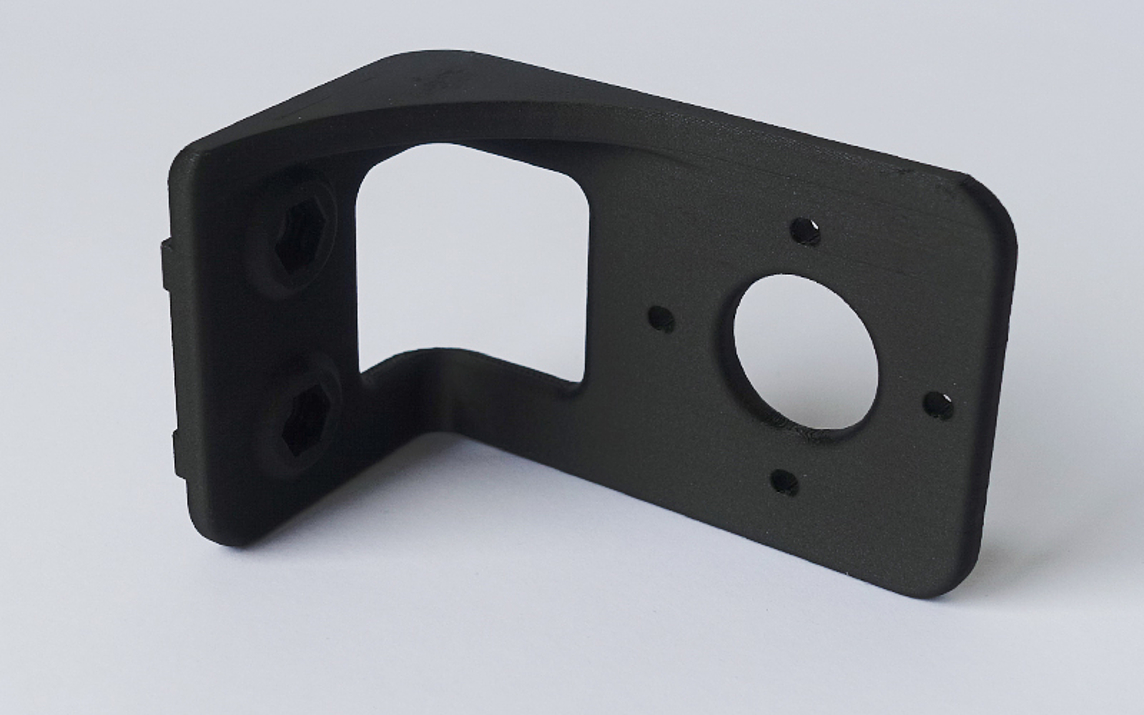
New possibilities with 3D printing
We print for you
With our new 3D printer we are particularly flexible and can produce complex parts for you in almost any conceivable shape.
The advantages are manifold:
- Short production times
- Short-term design changes possible without any problems
- Low development and production costs
- Optimal for prototypes, special designs and small batches
- Complex geometries can be realized
- Less waste thanks to additive manufacturing
Is that what you are looking for?
Just ask us:
![[Translate to EN:] Silvan Mesmer](/fileadmin/_processed_/f/6/csm_Spuhl-Lohnfertigung-Silvan-Mesmer_90d4d05b3e.jpg)
Silvan Mesmer
Technical contact SPS
Phone
+41 71 292 12 32
E-Mail
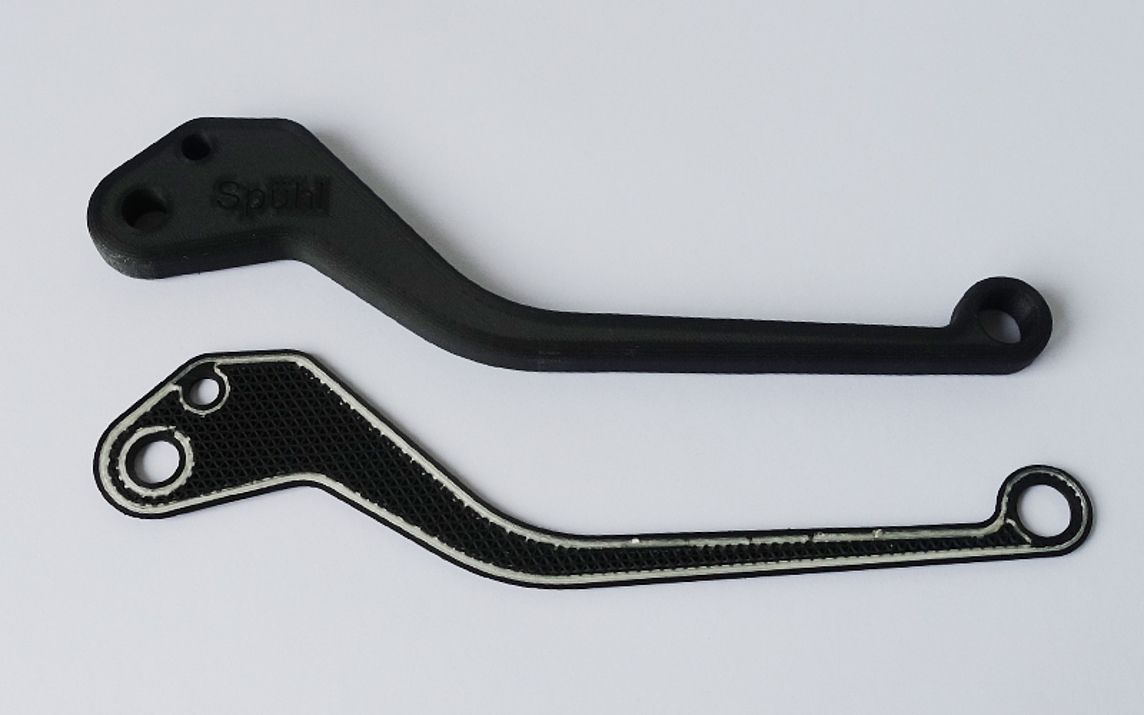
Fiber-Reinforced 3D Printed Parts
Our 3D printing process allows lightweight components made of thermoplastic materials to be produced quickly and proficiently with a high level of rigidity. The 3D printed parts are reinforced by inserting continuous technical fibers so that they can easily withstand high industrial loads.
The fiber reinforcement can be incorporated individually: the position, number of layers and angle of orientation of the fibers can be selected in such a way that the reinforcement is adjusted to suit the application.
FEM-Engineering in 3D Printed Parts
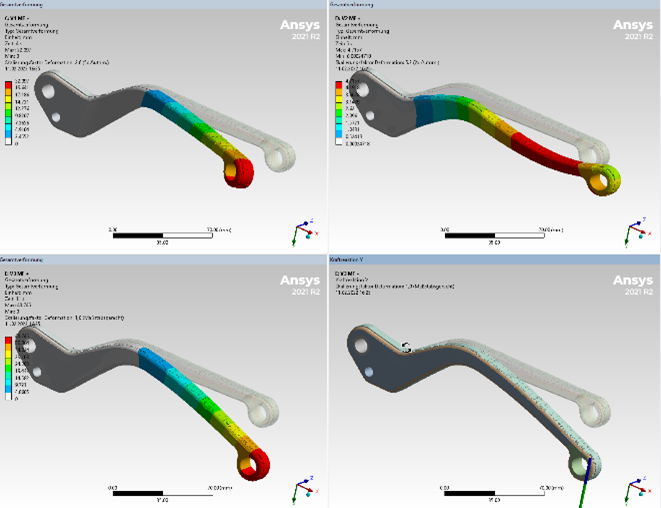
We are able to calculate the component rigidity and the deformation behavior of unreinforced and fiber-reinforced components using modern FEM methods - even before production takes place.
This makes it easy to optimize components specifically for the application. The most important aspect is: you know in advance that the component is suitable for the intended use and save yourself from having to make several attempts.
FEM Calculation Process
- CAD data for the planned component
- Specification of the intended use with the corresponding load
- Creation of a production proposal for 3D printing
- Integration of the fiber reinforcement
- Construction of the calculation model based on the production data
- FEM calculation (finite element method)
- Optimization of the component’s geometry, relocation of fibers, internal component structure, etc.
- 3D printing of the component based on the optimized component shape
- Optional: verification by means of a test using a measurement device














